IP Address Kya Hota Hai ?
Socho ki har device jo internet pe connected hai, ek ghar jaisa hai. Agar tumhe apne dost ko letter bhejna hai jo kisi specific ghar me rehta hai, toh tumhe uska address chahiye hoga. Digital duniya me ye address IP (Internet Protocol) Address kehlata hai.
Ye ek unique number hota hai jo periods (IPv4) ya colons (IPv6) se separate hota hai, aur har device ko allocate kiya jata hai jo internet ya local network se connected hoti hai.
IP Address ki Definition :
IP Address (Internet Protocol Address) ek unique number hota hai jo kisi bhi device ko diya jata hai jo Internet Protocol ka use karke communication karti hai. Ye ek identifier ki tarah kaam karta hai jo devices ko network par data bhejne aur receive karne me madad karta hai, taaki data sahi destination tak pahunch sake.
Types of IP Address
IP addresses ko alag-alag tariko se classify kiya ja sakta hai, jaise ki unka structure, purpose, aur kis type ke network me use ho raha hai. Yahaan par IP addresses ki classifications ka ek breakdown diya gaya hai:
IPv4:
Ye sabse common type ka IP address hai. Isme 4 sets of numbers hote hain jo dots (.) se separate hote hain. Example: 192.158.1.38
Har set 0 se 255 tak ho sakta hai. IPv4 ka format 4 billion+ unique addresses support karta hai.
IPv4 Structure Breakdown:
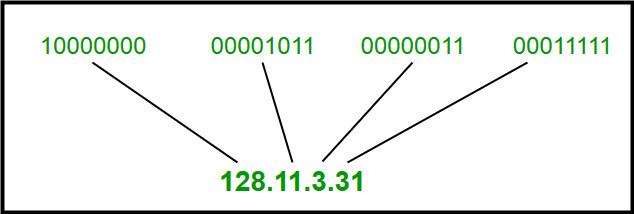
IPv4 address 4 octets ka combination hota hai. Ek octet 8 bits ka hota hai, aur har octet ki value 0-255 tak ho sakti hai.
✅ Example: 192.168.1.1
192→ First octet168→ Second octet1→ Third octet1→ Fourth octet
Har part ka ek alag role hota hai. Pehle 1-3 octets network ko represent karte hain, aur last octet device (host) ko identify karta hai.
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) internet ka original addressing system hai, jo 1983 me introduce kiya gaya tha. Yeh 32-bit address scheme ka use karta hai, jo theoretically 4.3 billion+ unique addresses (2³²) generate kar sakta hai.
IPv4 addresses decimal format me dikhaye jate hain, jo 4 octets me divide hote hain aur dots (.) se separate hote hain.
✅ Example of IPv4 Address:192.168.1.1 (Jo aksar home networks me use hota hai)
IPv4 aaj bhi sabse zyada use hone wala protocol hai, lekin limited addresses hone ki wajah se IPv6 ko develop kiya gaya hai. 🚀

IPv6:
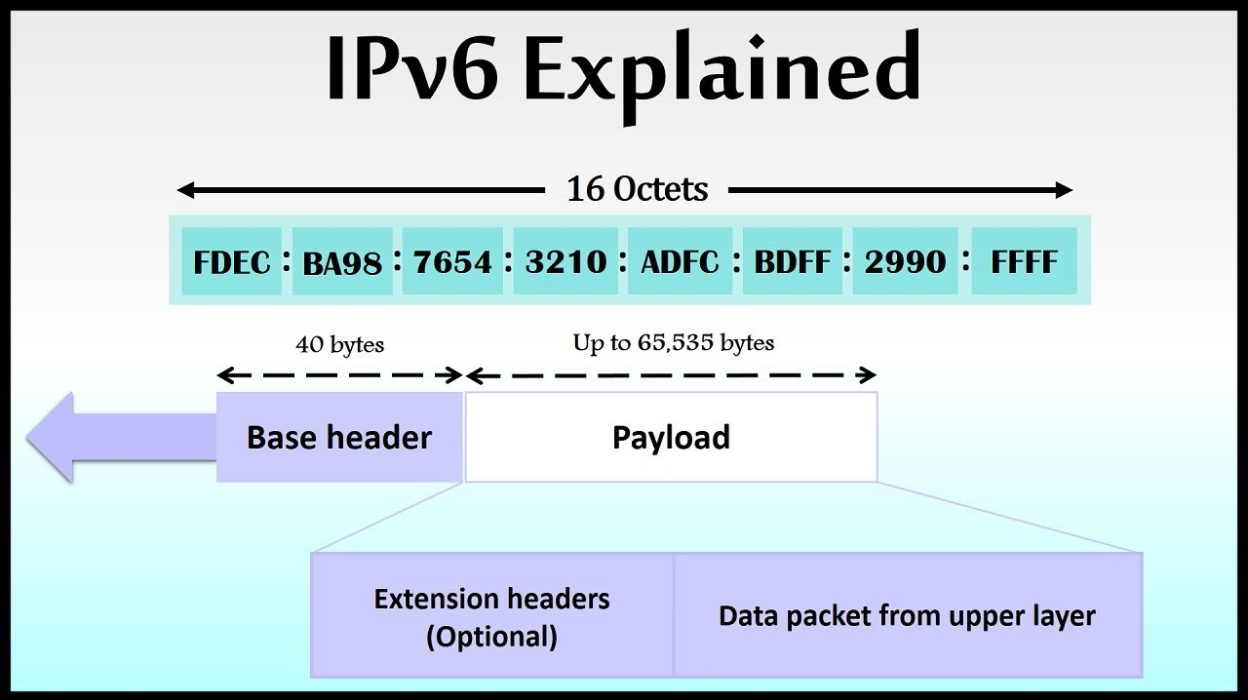
IPv6 addresses ko IPv4 address ki kami (shortage) ko solve karne ke liye banaya gaya tha. IPv6 128-bit ka hota hai, jo IPv4 ke 32-bit ke comparison me bahut zyada addresses generate karne ki capability rakhta hai.
Ye addresses 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits me likhe jate hain, aur colons (:) se separate hote hain. Har group 16 bits ka hota hai.
✅ Example of IPv6 Address:2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
🔹 Breakdown:
2001→ First 16-bit block0db8→ Second 16-bit block85a3→ Third 16-bit block0000→ Fourth 16-bit block0000→ Fifth 16-bit block8a2e→ Sixth 16-bit block0370→ Seventh 16-bit block7334→ Eighth 16-bit block
IPv6 ka sabse bada advantage ye hai ki isme unlimited number of devices ko connect karna possible ho jata hai, jo aaj ke expanding internet infrastructure ke liye zaroori hai. 🚀
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 Kya Hai?
IPv4, yaani Internet Protocol version 4, internet ka original addressing system hai jo 1983 me introduce kiya gaya tha. Ye 32-bit address scheme use karta hai, jo theoretically 4 billion+ unique addresses (2³²) provide kar sakta hai. IPv4 addresses decimal format me dikhte hain, jo dots (.) se separate 4 octets me divided hote hain.
✅ Example: 192.168.1.1 (Jo aksar home network me use hota hai)
IPv4 Address Format
IPv4 address 32-bit ka hota hai, jo binary digits me hota hai aur dots (.) se separate hota hai.
Characteristics of IPv4
32-bit Address Length:
IPv4 me 32-bit ka address hota hai, jo approx 4.3 billion unique addresses provide karta hai.Dot-Decimal Notation:
IP addresses 4 decimal numbers me likhe jate hain, jo dots (.) se separate hote hain. Example:192.168.1.1Packet Structure:
IPv4 packet header aur payload se milke banta hai. Header me routing aur delivery ke liye zaroori information hoti hai.Checksum Fields:
IPv4 header me checksum hota hai jo header integrity check karne ke liye use hota hai.Fragmentation:
Agar packet ka size MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) se bada hota hai, toh routers packets ko fragment kar sakte hain.Address Resolution Protocol (ARP):
ARP ka use IP addresses ko hardware (MAC) addresses me map karne ke liye hota hai.Manual and DHCP Configuration:
IPv4 manual configuration aur DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) dono support karta hai.Limited Address Space:
IPv4 ke limited addresses hone ki wajah se hi IPv6 ka development hua, taaki zyada devices connect ho sakein.Network Address Translation (NAT):
NAT ka use ek private network ke multiple devices ko ek single public IP address share karne ke liye hota hai.Security:
IPv4 me inherent security features nahi hoti, isliye secure communication ke liye IPSec jaise protocols use karne padte hain.
Drawbacks of IPv4
Limited Address Space:
IPv4 me kam addresses available hain, jo aaj ke time me growing number of devices ke liye sufficient nahi hain.Complex Configuration:
IPv4 ki configuration manual ya DHCP se hoti hai, jo time-consuming aur error-prone ho sakti hai.Less Efficient Routing:
IPv4 header complex hota hai, jo data processing aur routing ko slow kar sakta hai.Security Issues:
IPv4 me built-in security features nahi hain, isliye extra security measures lagane padte hain.Limited Support for QoS (Quality of Service):
IPv4 me specific data types ko prioritize karne ki limited capabilities hoti hain, jo real-time applications jaise video streaming aur VoIP ke performance ko affect kar sakti hain.Fragmentation:
IPv4 me routers packets ko fragment kar sakte hain, jo inefficiencies aur data loss ka risk badha sakta hai.Broadcasting Overhead:
IPv4 me broadcasting se network me unnecessary traffic aur performance issues ho sakte hain.
IPv4 ke ye sab features aur drawbacks milke is protocol ko define karte hain, lekin limited address space ki wajah se IPv6 ki zarurat padi.

IPv6 Kya Hai?
Aaj ke time me sabse common Internet Protocol versions me se ek IPv6 hai. Ye zyada tar mobile phone markets me use ho raha hai aur deploy kiya ja raha hai. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) ne December 1998 me IPv6 design kiya tha, taki IPv4 ke limited addresses ka solution nikala ja sake, kyunki globally internet users exponentially badh rahe the.
IPv6 ka Full Form → Internet Protocol version 6
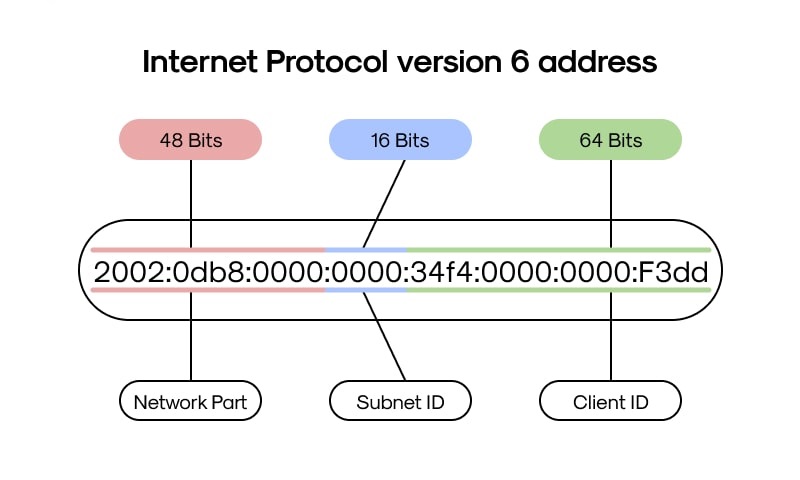
Ye naya version hai jo IPv4 se better hai, kyunki ye zyada efficient aur complex networks ko support karta hai. IPv6 8 groups of hexadecimal numbers me likha jata hai, jo colons (:) se separate hote hain.
✅ IPv6 ko 128-bit ke 0s aur 1s me likha ja sakta hai.
IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 ka address 128-bit ka hota hai, jo 8 hexadecimal numbers ke groups me likha jata hai aur colons (:) se separate hota hai.
IPv4 se IPv6 par Switch Karne ke Strategies
Dual Stacking:
Devices IPv4 aur IPv6 dono ek saath use kar sakti hain. Isse wo dono networks aur devices se connect ho sakti hain.Tunneling:
IPv6 users IPv4 network ke through data bhej sakte hain, jaise ek “tunnel” create karna jisme IPv6 traffic older IPv4 system ke andar se pass ho.Network Address Translation (NAT):
NAT ka use IPv4 aur IPv6 ke beech communication establish karne ke liye hota hai. Yeh addresses ko translate karta hai, taki dono versions ek dusre ko samajh sakein.
Characteristics of IPv6
✅ 1. 128-bit Addressing:
IPv6 me 128-bit ka address space hota hai, jo IPv4 ke 32-bit system se bohot zyada bada hai.
✅ 2. Hexadecimal Addressing:
IPv6 numbers aur letters (hexadecimal format) ka combination use karta hai, jo colons (:) se separate hote hain.
✅ 3. Efficient Header:
IPv6 header me kam fields hote hain, jo routers ke liye processing fast bana dete hain.
✅ 4. No Broadcasting:
IPv6 Unicast, Multicast, aur Anycast support karta hai, lekin Broadcasting nahi hoti, jo network traffic reduce karta hai.
✅ 5. Flexible Subnetting (VLSM):
IPv6 Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) allow karta hai, jo network size ke hisaab se subnet divide karne me help karta hai.
✅ 6. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP):
IPv6 me ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) ke jagah NDP ka use hota hai MAC address resolution ke liye.
✅ 7. Advanced Routing Protocols:
IPv6 OSPFv3 aur RIPng jaise better routing protocols use karta hai.
✅ 8. Auto-Configuration (SLAAC & DHCPv6):
IPv6 devices automatically apna IP address assign kar sakti hain (SLAAC) ya phir DHCPv6 ka use kar sakti hain manual control ke liye.
✅ 9. Fragmentation at Sender Side:
IPv6 me routers fragmentation nahi karte, balki sender device pe fragmentation hoti hai, jo data transfer speed improve karta hai.
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 ka 32-bit address length hota hai. | IPv6 ka 128-bit address length hota hai. |
| Manual aur DHCP address configuration support karta hai. | Auto-configuration aur renumbering support karta hai. |
| End-to-end connection integrity possible nahi hai. | End-to-end connection integrity possible hai. |
| 4.29 × 10⁹ addresses generate kar sakta hai. | 3.4 × 10³⁸ addresses generate kar sakta hai. |
| Security applications pe depend karti hai. | IPv6 me IPSEC inbuilt security feature hai. |
| Decimal format me address representation hoti hai. | Hexadecimal format me address likha jata hai. |
| Fragmentation sender aur forwarding routers dono karte hain. | Fragmentation sirf sender karta hai. |
| Packet flow identification available nahi hoti. | Packet flow identification available hai, jo flow label field ka use karta hai. |
| Checksum field available hota hai. | Checksum field available nahi hota. |
| Broadcast message transmission scheme use hoti hai. | Multicast aur Anycast message transmission support karta hai. |
| Encryption aur Authentication provide nahi karta. | Encryption aur Authentication provide karta hai. |
| IPv4 ka header size 20-60 bytes hota hai. | IPv6 ka header size fixed 40 bytes hota hai. |
| IPv4 ko IPv6 me convert kiya ja sakta hai. | Har IPv6 ko IPv4 me convert nahi kiya ja sakta. |
| IPv4 addresses 4 fields me hote hain jo dots (.) se separate hote hain. | IPv6 addresses 8 fields me hote hain jo colons (:) se separate hote hain. |
| IPv4 addresses 5 classes me divide hote hain (Class A, B, C, D, E). | IPv6 me IP address classes nahi hoti. |
| IPv4 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) support karta hai. | IPv6 VLSM support nahi karta. |
Example: 66.94.29.13 | Example: 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB |
Benefits of IPv6 over IPv4
Larger Address Space:
IPv6 ka 128-bit IP Address hai, jo IPv4 ke 32-bit address se kaafi bada hai. Isse IP connected devices ka address space kaafi zyada ho jata hai, jo future growth ke liye zaroori hai.Improved Security:
IPv6 me built-in security features hote hain, jaise ki Data Authentication aur Data Encryption, jo internet connection ko zyada secure banata hai.Simplified Header Format:
IPv6 ka header format IPv4 ke comparison me simpler aur effective hai, jo cost-effective hai aur internet connection speed ko bhi increase karta hai.Prioritize QoS (Quality of Service):
IPv6 me stronger aur reliable support hai for QoS features, jo websites ke traffic ko manage karne me madad karta hai aur audio/video quality improve karta hai.Improved Support for Mobile Devices:
IPv6 me mobile devices ke liye better support hai, jo quick aur secure connections ko possible banata hai, better than IPv4.
Why IPv4 is Still in Use?
Infrastructure Compatibility:
Bohot se systems aur devices IPv4 pe built hain, aur inhe IPv6 ko support karne ke liye significant updates ki zarurat hai, jaise ki routers, switches, aur computers ko update karna.Cost of Transition:
IPv6 me shift karna kaafi expensive aur complex ho sakta hai, kyunki isme hardware updates, software upgrades, aur training ki zarurat padti hai.Lack of Immediate Need:
Techniques jaise ki NAT (Network Address Translation) IPv4 ki life ko extend kar deti hain, kyunki yeh multiple devices ko ek single public IP address share karne ki permission deti hain, isliye IPv6 transition ki urgency kam ho jati hai.Coexistence Strategies:
Aise technologies available hain jo IPv4 aur IPv6 ko simultaneously chalne deti hain. Isse organizations gradually IPv6 adopt kar sakti hain, while maintaining their existing IPv4 systems.Slow Global Adoption:
IPv6 adoption globally slow hai, isliye IPv4 ka support abhi bhi important hai for global connectivity.Lack of Visible Benefits:
Bohot se users aur organizations ko IPv6 ka immediate benefit nahi dikhta, especially agar unhe IP address shortage ka issue nahi ho raha, isliye unke liye IPv6 upgrade karne ka incentive kam hota hai.
2. Based on Usage (Public vs. Private)
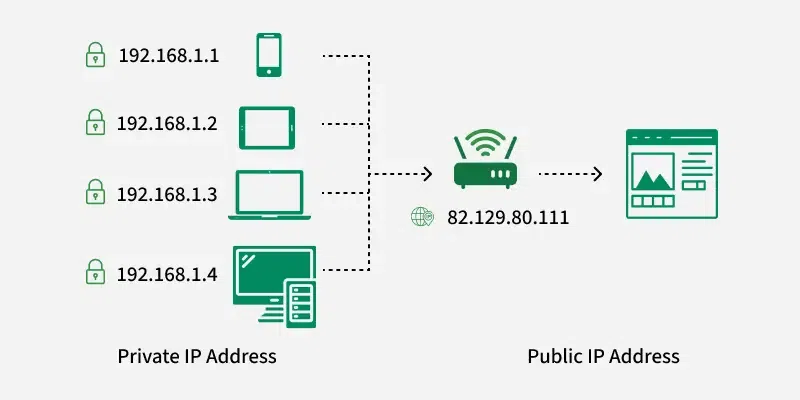
Public IP Addresses
- Uniqueness: Har ek public IP address globally unique hota hai. Internet pe koi bhi do devices ek hi waqt pe same public IP address nahi rakh sakte.
- Accessibility: Public IP address wale devices ko directly kahi se bhi internet se access kiya ja sakta hai, jab tak koi firewall ya security settings is access ko block na kar dein.
- Assigned by ISPs: Public IP addresses ko Internet Service Providers (ISPs) assign karte hain. Jab aap ISP se internet se connect karte ho, aapke device ya router ko ek public IP milta hai.
- Types: Public IP addresses do types ke hote hain:
- Static: Jo device ko permanent assign hota hai.
- Dynamic: Jo temporarily assign hota hai aur waqt ke saath change ho sakta hai.
Example Use: Public IP addresses ka use un devices ke liye hota hai jo directly accessible hone chahiye, jaise web servers, email servers, ya koi bhi device jo internet se directly accessible ho. Maan lijiye aap apne ghar me apna website server host kar rahe ho, toh aapke ISP ko apke server ko public IP address assign karna padega taaki duniya bhar ke users aapki site ko access kar sakein.
Private IP Addresses
- Not globally unique: Private IP addresses sirf apne local network me unique hote hain. Alag-alag private networks ek hi range ke IP addresses use kar sakte hain bina kisi conflict ke.
- Local communication: Yeh addresses sirf same network me devices ke beech communication ke liye use hote hain. Yeh directly internet pe devices ke saath communicate nahi kar sakte bina kisi Network Address Translation (NAT) mechanism ke.
- Defined ranges: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) ne kuch specific IP address ranges reserve kiye hain jo private use ke liye hain:
- IPv4:
- 10.0.0.0 se 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 se 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 se 192.168.255.255
- IPv6: FD ya FC se start hone wale addresses.
- IPv4:
Example Use: Ek typical home network me, router har device (smartphone, laptop, smart TV, etc.) ko private IP address assign karta hai. Yeh devices apne private IPs ko use karte hain ek doosre se aur router se communicate karne ke liye. Router phir NAT ka use karke in devices ko internet pe public IP address ke through access karne deta hai.
3. Based on Assignment Method (Static vs. Dynamic)
Static IP Addresses:
- Permanent Assignment: Static IP addresses permanently assign hote hain ek device ko. Yeh un devices ke liye important hote hain jo constant address require karte hain, jaise servers ya koi device jo hamesha accessible hona chahiye.
- Reliable for Network Services: Static IP addresses reliable hote hain un network services ke liye jo regular access require karti hain, jaise websites ya remote management.
Dynamic IP Addresses:
- Temporary Assignment: Dynamic IP addresses temporarily assign kiye jate hain ek available address pool se, jo Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ke through hota hai.
- Cost-effective: Yeh cost-effective aur efficient hote hain providers ke liye. Yeh un consumer devices ke liye perfect hain jo permanent address ki zarurat nahi rakhte, jaise smartphones, laptops, etc.
